Glossary of Terms
To better understand your coverage and make the best plan selection for your specific needs, it’s helpful to be familiar with health care vocabulary. Take a moment to review these terms, which may be referenced throughout this Benefits Website. To learn more about the important terms used in the health benefit industry click on the image below or continue reading the text.
Common Health Benefit Terms
Allowed Amount – Maximum amount on which payment is based for covered medical services. If an out-of-network provider charges more than the allowed amount, you may have to pay the difference.
Balance Billing – When a healthcare provider bills a patient for the difference between the insurance carrier’s allowed amount and the provider’s charge. If the provider’s charge is $250 and the allowed amount is $170, the provider may bill the patient for the remaining $80. An in-network provider cannot balance bill you for the covered services.
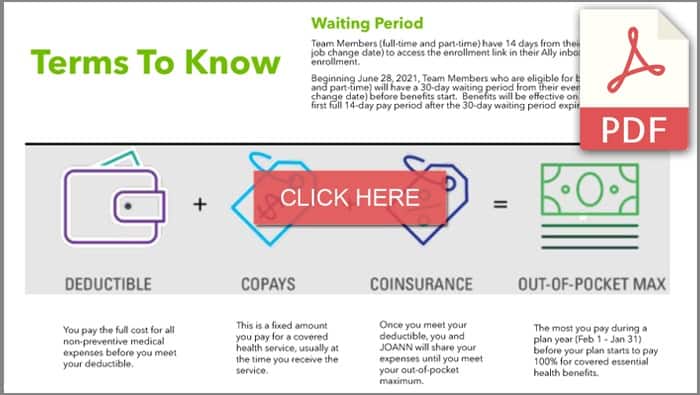
Coinsurance – Your share of the cost of a covered medical service calculated as a percent of the allowed amount for the service. The medical plan pays the rest of the allowed amount. Review the plans carefully to understand your responsibility. You are responsible for the coinsurance until you reach your plan’s out-of-pocket maximum.
Copay – A copay is a fixed amount, which you pay at the time of service. For specific medical services, you may have a copay, a specific charge required by your insurance company for certain medical, dental, or vision visits. While copays do not usually count toward the deductible, they do count toward your out-of-pocket maximum. Copays are most common for prescription drugs, office visits, urgent care, and emergency room visits.
Deductible – The amount you must pay out-of-pocket for eligible expenses before the health plan begins to pay benefits. Your plan will not pay anything for certain medical services until you have met your deductible amount. The deductible may not apply to all services, for example, services that are covered by a copay.
Explanation of Benefits (EOB) – An EOB explains how much you owe, the total cost of care, how much your plan paid, and the amount an in-network doctor or other healthcare professional is allowed to charge a member.
Formularies – A formulary is a list of approved drugs that your insurance company agrees to help cover.
Flexible Spending Account (FSA) – An arrangement that provides a mechanism for participants to pay for certain medical and/or dependent care expenses on a pre-tax basis.
High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) – A HDHP provides coverage for doctor visits, hospital care, emergency care, and prescription drugs. You must meet the deductible before the plan begins to pay. To help you meet out-of-pocket costs, such as your deductible, you can open a Health Savings Account (HSA). You can contribute pre-tax dollars to pay for eligible medical expenses tax-free.
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) – An HMO plan offers access to doctors and specialists within the plan’s network only. If you visit a provider outside of the network, you will be responsible for the full cost of services received. There is no deductible to satisfy and you typically pay a copay for medical services. You will need to select a Primary Care Physician (PCP) to coordinate your health care, including referrals to specialists.
Health Savings Account (HSA) – An HSA is a tax-advantaged medical savings account available to those enrolled in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP). Funds can be used to pay for qualified healthcare expenses per IRS guidelines. The funds contributed to an account are not subject to federal income tax at the time of deposit.
In-Network Provider – An in-network provider is a healthcare provider that has a service contract with your health insurance company or health plan to provide services to you at a discount. This enables participants to receive care at a reduced rate compared to care received by out-of-network providers.
Out-of-Network Provider – An out-of-network provider does not have a service contract with your health insurance company or health plan. Your out-of-pocket costs may increase, and services may be subject to balance billing.
Out-of-Pocket Maximum – The most you pay during the plan year before your plan begins to pay 100% of the allowed amount. This limit does not include your premium or balance-billed charges.
Participant – Employees and our beneficiaries: the spouse and kids. The greatest responsibility of a defined-contribution plan such as a 401(k) falls to the participant.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) – A PPO plan gives you flexibility to choose an in-network or out-of-network provider. PPO plans may have lower deductibles and copays but higher employee premiums.
Preauthorization – A determination by the health plan that a medical service, prescription drug, or durable medical equipment is medically necessary.
Preferred Provider – A preferred provider is a provider who has a service contract with your health insurance company or health plan and has a cost and quality designation.
Prescription Drug Coverage – A health insurance carrier’s formulary is a list of FDA approved drugs covered under the medical plan. Each drug is classified into a tier and each tier determines the cost you will pay for the drug.
Preventive Services – The set of services, such as routine screenings and shots, that support maintaining your health. These services are covered in full by your health plan and are based on Federal Guidelines. They must be administered by an in-network physician. Consult your insurance provider for a list of preventive services.
Primary Care Physician – A physician including an MD, DO, Internists, Family Practitioner, GP, OB/GYN, and Pediatrician who provides a range of medical services.
Specialist – A physician who focuses on a specific area of medicine or group of patients to diagnose, manage, prevent, or treat certain types of symptoms and conditions.
Usual, Customary & Reasonable Charges (UCR) – The calculation by a health care provider of what they determine is the appropriate fee to pay for a specific health care service.
Common Health Plan Acronyms
ADA – Americans with Disabilities Act
AD&D – Accidental Death and Dismemberment
CDHP – Consumer Driven High-deductible Plan
COBRA – Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act
DCAP – Dependent Care Assistance Program
EAP – Employee Assistance Program. Provides counseling and other services to employees.
EOB – Explanation of Benefits. Issued by insurance companies to participants to explain what amount of their medical expenses was covered.
EOI – Evidence of Insurability. Sometimes called evidence of good health, often required by insurers before issuing an LTD or GTL policy.
FFS – Fee For Service
FICA – Federal Insurance Contribution Act. Refers to Social Security and Medicare taxes.
FSA – Flexible Spending Account
GTL Insurance – Group Term Life Insurance
HDHP – High Deductible Health Plan
Health FSA – A Flexible Spending Account (FSA) under which participants may obtain reimbursement for medical expenses.
HIPAA – Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
HMO – Health Maintenance Organization
HRA – Health Reimbursement Arrangement
HSA – Health Savings Account
LTD Plan – Long-Term Disability Plan. A plan that provides a partial income-replacement benefit to an employee unable to work because of a disability.
MSA – Medical Savings Account. Also known as an Archer MSA.
MSP Rules – Medicare Secondary Payer Rules. Laws that require Medicare to be the secondary payer in most situations where a group health plan or private insurance carrier also provides coverage.
OOPM – Out-of-Pocket Maximum
PCE – Preexisting Condition Exclusion
PHI – Protected Health Information
PPO – Preferred Provider Organization
SMM – Summary of Material Modifications. An ERISA-required summary of plan changes that a plan sponsor must distribute to participants and beneficiaries.
SPD – Summary Plan Description. An ERISA-required plan summary that must be furnished to participants and beneficiaries.
STD – Short-Term Disability
TPA – Third-Party Administrator